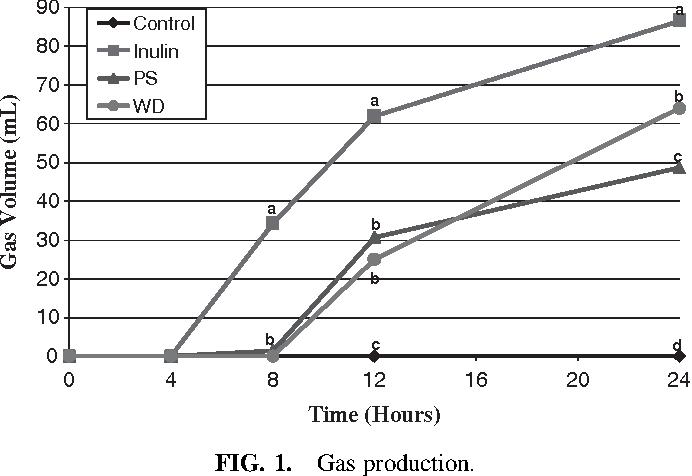
I just replied to a post with this information which might spark some responses......
I had to include the graph because it really made me laugh! (PS = psyllium, WD = wheat dextrin)
The serious bit: -
Inulin is a type of fructo-oligosaccharide, or FOS, that helps to feed the "friendly" bacteria in your gastrointestinal tract, explains the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Inulin is sometimes called a "prebiotic" and is found naturally in certain foods like asparagus, soybeans, leeks and onions. Psyllium seeds and seed husks come from the Plantago ispaghula and P. ovata plants, and they're typically used for their high fiber and mucilage content, says the University of Michigan Health System. Psyllium's fiber and mucilage offers bulk-forming laxative effects, as well as gastrointestinal-soothing, cholesterol-lowering and blood sugar-regulating actions.
Effects
Both inulin and psyllium might help control your blood-sugar levels if you have diabetes, as well as lower high triglycerides, according to the University of Michigan Health System. Both substances may also help treat high cholesterol, irritable bowel syndrome and diarrhea. Specifically, inulin and other FOS are sometimes used to relieve traveler's diarrhea, notes the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center. Inulin could also help to prevent eczema, while psyllium might help treat constipation and diverticular disease. Other potential uses for psyllium include helping to reduce the risks of colon cancer and heart disease, as well as helping to treat hemorrhoids, hypertension and inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, says the University of Maryland Medical Center. Talk with your physician before taking inulin or psyllium for any health purpose.
Potential
Inulin may possibly help support your health before and after undergoing surgery, notes the University of Michigan Health System. Psyllium might have the potential to promote weight loss by reducing hunger, says the University of Maryland Medical Center. Psyllium could also provide benefits if you have atherosclerosis or constipation related to Parkinson's disease. No conclusive medical research supports the use of inulin or psyllium for any of these purposes, however.
Dosages
You might take 1/2 to 2 teaspoons of psyllium seed mixed with 1 cup of warm water each day, or up to four doses per day, according to the University of Maryland Medical Center. You must drink the psyllium mixture immediately after mixing it, before it becomes too thick. Alternatively, you could take 2,000 to 3,000 mg of inulin each day, or as much as 8 to 20 grams daily to help treat diabetes, high triglycerides or high cholesterol levels, says the University of Michigan Health System. Ask your physician about the dosage that's right for you before taking psyllium or inulin.
Warning
Both inulin and psyllium can cause gas and bloating. Both substances may also cause allergic reactions in some people, although such adverse reactions are rare, says the University of Michigan Health System. If you have chronic constipation, uncontrolled diabetes or irritable bowel syndrome, take psyllium only under the close supervision of a health care professional. Also, psyllium may be unsafe if you have difficulty swallowing, esophageal stricture, or gastrointestinal tract or bowel obstructions, warns the University of Maryland Medical Center. Psyllium could interact negatively with certain medications, such as Tegretol, diabetes drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, digoxin and lithium.