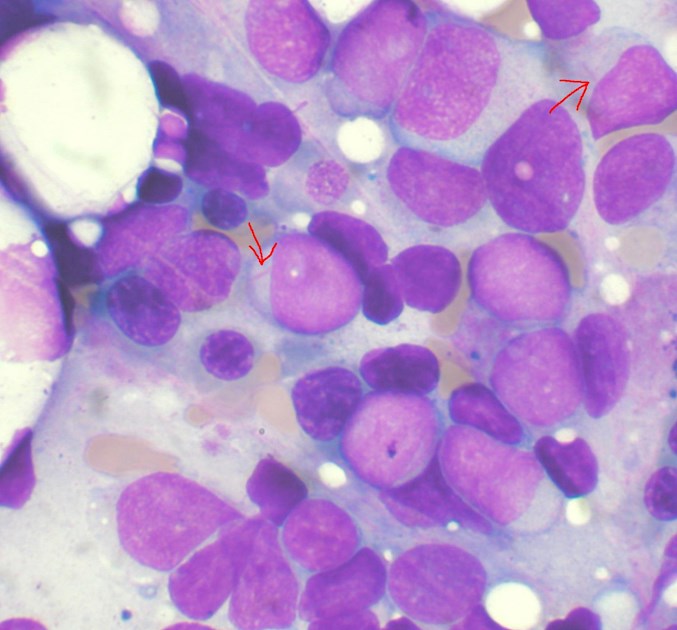
Bone marrow aspirate showing Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML). Several blasts have Auer rods. Wikipedia
This article out of the University of Montreal seems to hold some promise for the treatment of AML. Rather than just posting a link I thought it might be easier for all to read this extract simply by pasting it here... Reference below of course...
**
A molecular process involved in the action of anti-leukemia drugs has been discovered at Université de Montréal's Institute for Research in Immunology and Cancer (IRIC). While calling into question a central tenet of oncology, this discovery, published today in the journal Cancer Cell, also holds promise for the development of effective treatments in the near future.
Headed by Dr. Guy Sauvageau, principal investigator with IRIC's Molecular Genetics of Stem Cells Research Unit, the IRIC study focused specifically on acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common type of leukemia in adults. A cancer that originates in blood stem cells, AML strikes over 2,000 Canadians a year and is the most lethal form of leukemia. Even after chemotherapy and bone marrow transplants, life expectancy is less than three years in individuals with certain genetic profiles.
5,000 drugs tested
Before discovering new avenues for treatment, Dr. Sauvageau and his team first faced the enormous task of identifying the genes associated with myeloid leukemia. Working together with researchers at the Quebec Leukemia Cell Bank, particularly its director Josée Hébert, also a professor in UdeM's Faculty of Medicine, they were able to sequence the genetic profiles of nearly 700 patients with acute myeloid leukemia. They then tested the effects of approximately 5,000 drugs on the various forms of myeloid leukemia affecting these patients, whose cells were grown in vitro.
"It's important to understand that both myeloid leukemia and lymphocytic leukemia are a combination of approximately twenty different genetic diseases," explained Sauvageau.
"What we call 'leukemia' is actually the group of symptoms caused by these diseases. We thus had to test these 5,000 drugs on several AML subtypes in order to link each drug's effect to specific genes."
The drugs tested are not used specifically to treat leukemia, but rather are representative of the range of pharmaceutical treatments used to treat human diseases. Their effects were tested both on the cells of mice carrying the gene for acute myeloid leukemia and on human cells. A table comparing the effect of each drug on each AML subtype provided insight, through the genetic sequencing that revealed similarities in anomalies between the different types of AML, into why certain drugs act on certain AML subtypes and not on others.
Dr. Sauvageau and his team were thus able to determine that several of the molecules tested could have a complementary effect on various AML subtypes by acting in combination, leading to the potential for more effective treatments.
Mubritinib: A promising drug
One of these drugs, Mubritinib, a protein kinase inhibitor that regulates cellular metabolism and was originally developed for the treatment of breast cancer, showed particular promise. "We observed that Mubritinib had a therapeutic effect on certain subtypes of AML for which there are few effective treatments," explained Sauvageau, adding that the drug showed no toxicity in mice and little toxicity in human cells.
Mubritinib was subsequently modified at the IRIC before being patented. A large pharmaceutical company acquired the license and signed an agreement with the IRIC to mobilize an army of researchers with the aim of accelerating clinical trials in AML.
Revisiting the Warburg effect
In studying the electrochemical process behind Mubritinib's mode of action, Dr. Sauvageau's team stumbled upon another, unexpected, discovery. They observed that Mubritinib causes the death of cancer cells in an AML subgroup by arresting oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) of the tumor cell—i.e., its oxygenation.
"We've always assumed that, regardless of the type of cancer, tumor cells make little use of OXPHOS and produce most of their energy in the absence of oxygen," explained Dr. Sauvageau. "However, our work shows that oxidative phosphorylation is present in certain cells and that these cells use this process to produce their energy and proliferate. They die if OXPHOS is blocked," he added.
This discovery adds clarification, and even a caveat, to what is known in biochemistry as the Warburg effect. Accepted as a basic principle of oncology, the Warburg effect—named after its discoverer and the Nobel Prize in Medicine Otto Warburg—postulates that cancer cells produce their energy by breaking down glucose (glycolysis) without utilizing oxygen and that this is a key characteristic of cancer.
Sauvageau is very optimistic going forward. He believes that a new drug based on this study could reach the market within the next two to three years.
Best wishes
Steven
(Sydney)
REFERENCE
Irène Baccelli et al. Mubritinib Targets the Electron Transport Chain Complex I and Reveals the Landscape of OXPHOS Dependency in Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Cancer Cell (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.06.003