Some UK research and news of developments by the Cardiff CLL research team :
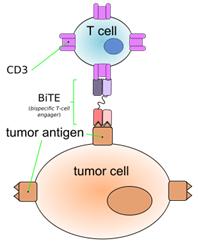
Blinatumomab is a bi-specific T-cell engager (BiTE).
Blinatumomab currently in trials treating B-NHL has shown clinical responses in patients with both indolent and aggressive diseases is now being looked at closely for CLL and is showing early in vitro results that it is effective at aiding our own depleted immune system against CLL Cells..
Researchers were concerned that the known immunodeficiencies displayed in CLL would reduce this effect with CLL tumour cells. However "Blinatumomab retains efficacy even in the presence of CLL activation and prosurvival signals"..
BLINATUMOMAB INDUCES AUTOLOGOUS T CELL KILLING OF CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA CELLS
by Ryan Wong, Chris Pepper, Paul Brennan, Dirk Nagorsen, Stephen Man, and Chris Fegan
published ahead of print June 28, 2013,
Abstract: haematologica.org/content/e...
“Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is an incurable B-cell malignancy that is associated with tumor cell-mediated T-cell dysfunction. It therefore represents a challenging disease for T-cell immunotherapeutics.
The CD19/CD3 bi-specific antibody construct blinatumomab (AMG103 or MT103) has been tested clinically in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukemia but has not been assessed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. We tested whether blinatumomab could overcome T cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia in vitro.
Blinatumomab was tested on PBMC from 28 patients (treatment naive and previously treated). T cell activation and function, as well as cytotoxicity against leukemic tumor cells were measured.
Blinatumomab induced T-cell activation, proliferation, cytokine secretion and granzyme B release in a manner similar to stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. However, only blinatumomab was able to induce tumor cell death and this was found to require blinatumomab-mediated conjugate formation between T-cells and tumor cells.
Cytotoxicity of tumor cells was observed at very low T cell:tumor cell ratios. A 3-D model based on confocal microscopy, suggested that up to 11 tumor cells could cluster round each T cell.
Importantly, blinatumomab induced cytotoxicity against tumor cells in samples from both treatment naïve and treated patients, and in the presence of co-culture pro-survival signals. The potent cytotoxic action of blinatumomab on tumor cells appears to involve conjugation of T cells with tumor cells at both the activation and effector stages. The efficacy of Blinatumomab in vitro, suggests that the bi-specific antibody approach may be a powerful immunotherapeutic strategy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.”
READ THE Full paper PDF here: haematologica.org/content/e...
.”
What is Blinitumomab - from wikipedia
“Blinatumomab (MT103) is a drug that has anti-cancer properties. It belongs to a new class of constructed monoclonal antibodies, bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), that exert action selectively and direct the human immune system to act against tumor cells. Blinatumomab specifically targets theCD19 antigen present on B cells.”
Blinatumomab enables a patient's T cells to recognize malign B cells. A molecule of blinatumomab combines two binding sites: a CD3 site for T cells and a CD19 site for the target B cells. CD3 is part of theT cell receptor. The drug works by linking these two cell types and activating the T cell to exert cytotoxicactivity on the target cell en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blina...
Nick