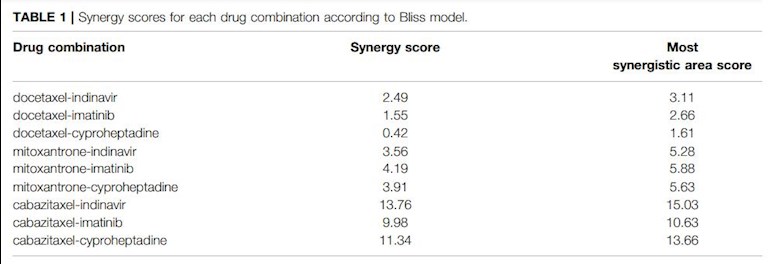
Prediction of Synergistic Drug Combinations for Prostate Cancer by Transcriptomic and Network Characteristics
Prostate cancer (PRAD) is a major cause of cancer-related deaths. Current monotherapies show limited efficacy due to often rapidly emerging resistance. Combination therapies could provide an alternative solution to address this problem with enhanced therapeutic effect, reduced cytotoxicity, and delayed the appearance of drug resistance. However, it is prohibitively cost and labor-intensive for the experimental approaches to pick out synergistic combinations from the millions of possibilities. Thus, it is highly desired to explore other efficient strategies to assist experimental researches. Inspired by the challenge, we construct the transcriptomics-based and network-based prediction models to quickly screen the potential drug combination for Prostate cancer, and further assess their performance by in vitro assays. The transcriptomics-based method screens nine possible combinations.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/339...
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Although the therapeutic effect of cyproheptadine in Prostate cancer has never been reported, the use of cyproheptadine in the treatment of multiple malignancies, such as myeloma, leukemia and hepatocellular carcinoma, to some extent suggest the effect of cyproheptadine in combating cancers. Therefore, it is reasonable for cyproheptadine-containing combinations to be potential for the Prostate cancer treatment.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For example: Efficacy of Cyproheptadine Monotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Bone Metastasis: A Case Report
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/347...
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cyproheptadine represents an attractive anticancer drug candidate, especially as it is already in clinical use as an anti-serotonin and appetite stimulant and is well tolerated and officially approved for years.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Serotonin is a growth factor for several human carcinomas, glioma and carcinoids. Serotonin is also involved in cancer cell migration, metastasis and angiogenesis. The levels of the monoamine in the tumor play a crucial role in cancer progression. Serotonin receptor expression becomes dysregulated in several cancers.