This begs the question - if these are not naturally occurring substances in our body - how the hell did they get into our brains? And what can we do about it?
NMDA is not an endogenous (native) substance. It's not found in our body tissue but rather synthesized as an excitotoxin for research into NMDA receptors. The natural ligand for NMDARs is Glutamate (and to a lesser extent, Aspartate) but the receptors also require a co-agonist Glycine or D-serine for activation. There are two separate sub-units. NR1 (which binds Glycine) and NR2 (binds Glutamate).
AMPA is not an endogenous (native) compound but a synthetic glutamate analog that specifically binds the AMPA receptor. Glutamate binds to the AMPA receptor as well. [The metabolite of Glyphosate is AMPA - the same neurotoxic AMPA we're discussing here.]
There are a number of reported endogenous Allosteric Modulators of NMDARs which include Magnesium and Zinc.
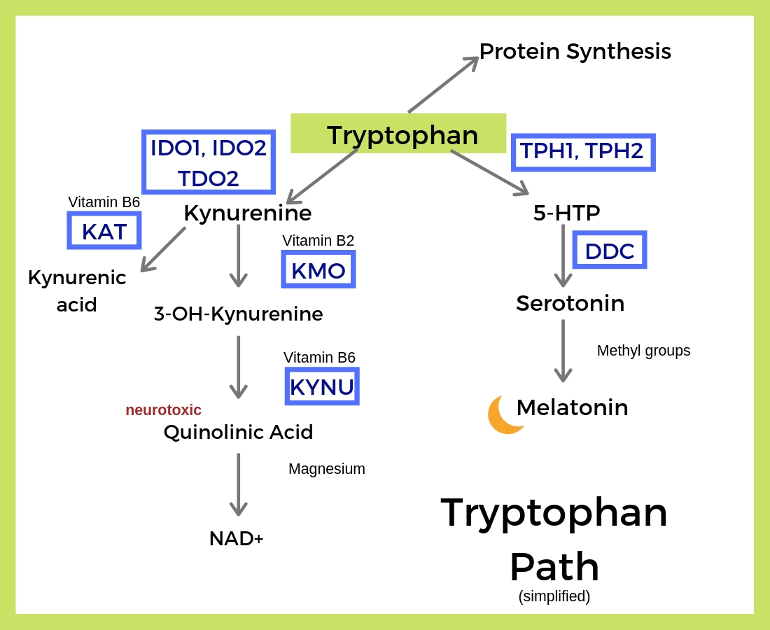
The only proposed endogenous antagonist for NMDARs (Glycine and Glutamate sites) and AMPARs is Kynurenic Acid [kynurenine] (a metabolite of Tryptophan) which also acts at the Kainate receptor.
brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare/...
Kynurenine pathway: The majority of tryptophan is converted into kynurenine. This can eventually lead to tryptophan being converted into niacin [B3]. ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/n...
Serotonin pathway: A little bit of the tryptophan you consume is used to make serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter in the brain and in the intestines. Serotonin is the precursor for melatonin, so tryptophan eventually can become melatonin. [Why would anyone take SSRIs?]
L-tryptophan is an essential amino acid that influences your mood, sleep, neurotransmitters, and immune response. Tryptophan is converted into serotonin, melatonin, quinolinic acid (neurotoxin), and niacin.
L-tryptophan is converted to melatonin in the GI-tract during the day when the pineal gland synthesis is inhibited.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/233...
L-tryptophan supplementation in Parkinson's Disease pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/274....
This site is a wealth of information including genetic variants and susceptibility to disease. If you're interested, and I am.
SE 🕊️