Wilmar M. Wiersinga
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2014) doi:10.1038/nrendo.2013.258 Published online 14 January 2014
Abstract
Abstract•
References•
Author information
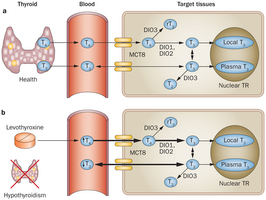
Impaired psychological well-being, depression or anxiety are observed in 5–10% of hypothyroid patients receiving levothyroxine, despite normal TSH levels. Such complaints might hypothetically be related to increased free T4 and decreased free T3 serum concentrations, which result in the abnormally low free T4:free T3 ratios observed in 30% of patients on levothyroxine. Evidence is mounting that levothyroxine monotherapy cannot assure a euthyroid state in all tissues simultaneously, and that normal serum TSH levels in patients receiving levothyroxine reflect pituitary euthyroidism alone. Levothyroxine plus liothyronine combination therapy is gaining in popularity; although the evidence suggests it is generally not superior to levothyroxine monotherapy, in some of the 14 published trials this combination was definitely preferred by patients and associated with improved metabolic profiles. Disappointing results with combination therapy could be related to use of inappropriate levothyroxine and liothyronine doses, resulting in abnormal serum free T4:free T3 ratios. Alternatively, its potential benefit might be confined to patients with specific genetic polymorphisms in thyroid hormone transporters and deiodinases that affect the intracellular levels of T3 available for binding to T3 receptors. Levothyroxine monotherapy remains the standard treatment for hypothyroidism. However, in selected patients, new guidelines suggest that experimental combination therapy might be considered.
nature.com/nrendo/journal/v...
Yes please, more tests