Neurodegenerative diseases are a wide class of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive nervous system dysfunction. These disorders include Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington’s disease (HD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) which are caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
It has been shown that glutamate excitotoxicity induced oxidative stress is linked to neurodegenerative diseases.
Growing evidence suggests that the mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by glutamate excitotoxicity-induced oxidative stress was associated with both acute and chronic neurodegenerative disorders.
We found that green tea polyphenols protected against glutamate induced neurotoxicity in the cortical neurons.
Furthermore, our results demonstrated that green tea polyphenols restored the dysfunction of mitochondrial pro- or antiapoptotic proteins Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 caused by glutamate. hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2...
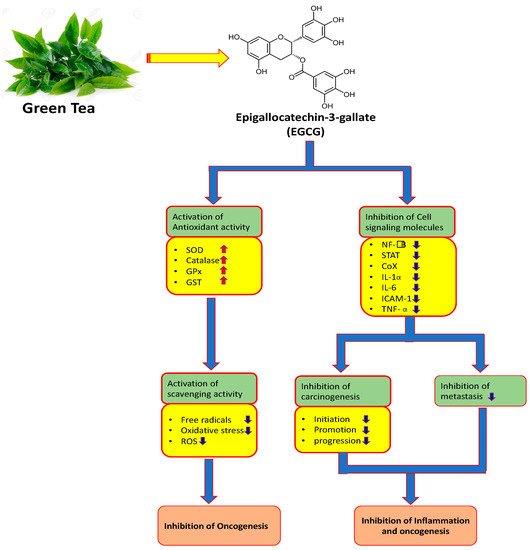
Green tea polyphenols have been found to be more antioxidant active than vitamin C and vitamin E. Furthermore, green tea polyphenols were shown to protect against beta-amyloid toxicity in the primary cultured cortical neurons.
WHAT IS IN GREEN TEA LEAVES THAT IS GOOD FOR YOU?
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
Epicatechin gallate (ECG)
L-theanine
Caffeine
THE BEST WAY TO CONSUME GREEN TEA POLYPHENOLS
With the catechins, EGCG, and ECG being the stars of this health-promoting, anti-aging story, one might assume taking a green tea extract is the best idea; however, in an article, the researchers recommend drinking green tea daily. The concern is that supplements could contain high doses of catechins which can pose a problem for the energy-making battery packs inside cells (mitochondria), including potential to cause cell death.
SE 🍵