From Detecting measurable residual disease beyond 10-4 through an IGHV leader-based NGS approach improves prognostic stratification in CLL
doi.org/10.1182/blood.20220...
Key Points from the German CLL Study Group
An academically-developed IGHV leader-based NGS assay can routinely detect and quantify MRD to 10-5 and beyond in CLL
MRD quantification below 10-4 using this assay improves prognostic stratification in CLL
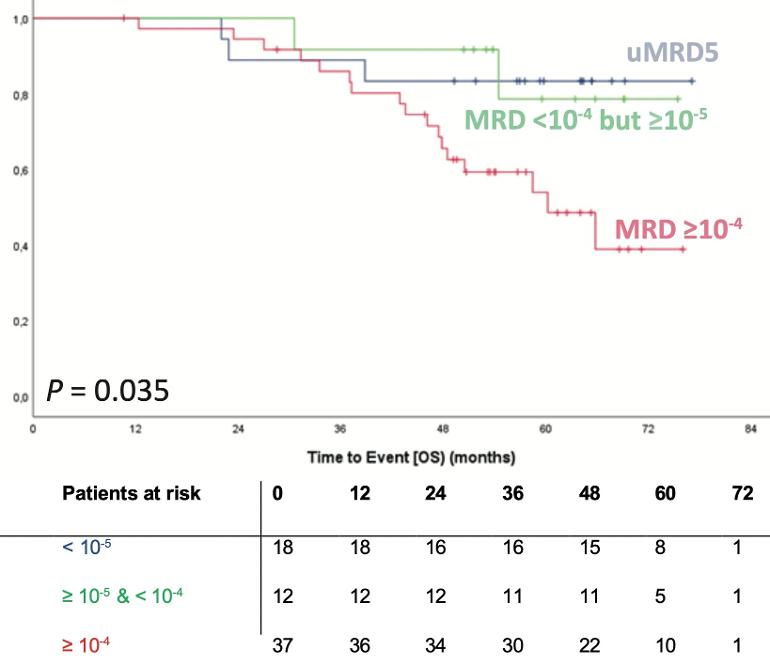
The sensitivity of conventional techniques for reliable quantification of minimal/measurable residual disease (MRD) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is limited to MRD 10-4. Measuring MRD <10-4 could help to further distinguish between CLL patients with durable remission and those at risk of early relapse. We here present an academically developed IGHV leader-based next-generation sequencing (NGS) assay for the quantification of MRD in CLL. We demonstrate, based on measurements in contrived MRD samples, that the linear range of detection and quantification of our assay reaches beyond MRD 10-5. If provided with sufficient DNA input, MRD can be detected down to MRD 10-6.
This work is important for two reasons:-
1) International cooperation on standardising uMRD testing
2) Per the attached plots Measuring MRD <10-4 could help to further distinguish between CLL patients with durable remission and those at risk of early relapse.So therapy can be refined, for example extending the treatment time, or switching from time limited to maintenance therapy.
This is an open (unlocked) post
Neil