Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson disease. A double-blind, randomized, controlled, crossover study (2017)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articl...
"This study demonstrates that the acute intake of MP powder at both high and low dose is non-inferior to dispersible levodopa/benserazide in terms of all efficacy and safety outcome measures."
LD : Levodopa
MP : Mucuna pruriens (variant utilis) 5.7% LD
MP-Hd : high-dose Mucuna pruriens powder
MP-Ldl: low-dose Mucuna pruriens powder
DDCI : dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor
AE : adverse event
* Objective:
To investigate whether Mucuna pruriens (MP), a levodopa-containing leguminous plant growing in all tropical areas worldwide, may be used as alternative source of levodopa for indigent individuals with Parkinson disease (PD) who cannot afford long-term therapy with marketed levodopa preparations.
* Methods:
We investigated efficacy and safety of single-dose intake of MP powder from roasted seeds obtained without any pharmacologic processing. Eighteen patients with advanced PD received the following treatments, whose sequence was randomized:
(1) dispersible levodopa at 3.5 mg/kg combined with the dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor benserazide (LD+DDCI; the reference treatment);
(2) high-dose MP (MP-Hd; 17.5 mg/kg);
(3) low-dose MP (MP-Ld; 12.5 mg/kg);
(4) pharmaceutical preparation of LD without DDCI (LD−DDCI; 17.5 mg/kg);
(5) MP plus benserazide (MP+DDCI; 3.5 mg/kg);
(6) placebo.
Efficacy outcomes were the change in motor response at 90 and 180 minutes and the duration of on state. Safety measures included any adverse event (AE), changes in blood pressure and heart rate, and the severity of dyskinesias.
* Results:
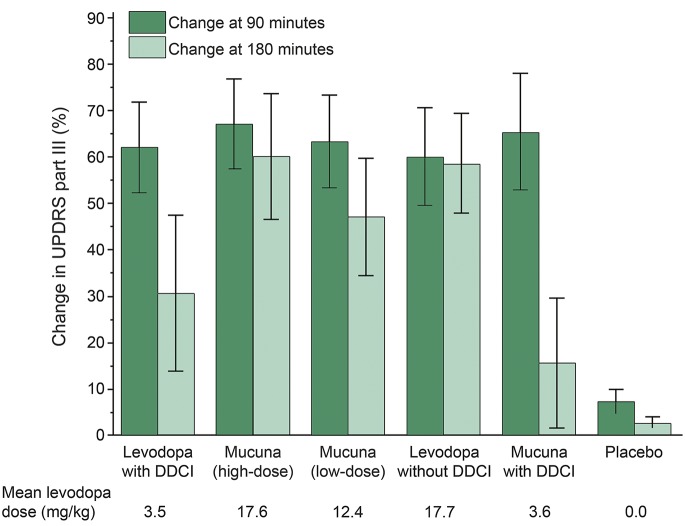
When compared to LD+DDCI, MP-Ld showed similar motor response with fewer dyskinesias and AEs, while MP-Hd induced greater motor improvement at 90 and 180 minutes, longer ON duration, and fewer dyskinesias. MP-Hd induced less AEs than LD+DDCI and LD−DDCI. No differences in cardiovascular response were recorded.
* Conclusion:
Single-dose MP intake met all noninferiority efficacy and safety outcome measures in comparison to dispersible levodopa/benserazide. Clinical effects of high-dose MP were similar to levodopa alone at the same dose, with a more favorable tolerability profile.
--------
"Both low-dose and high-dose MP were superior to placebo. Low-dose MP was associated with a motor response that was equivalent to the response to levodopa/benserazide, while high-dose MP induced a qualitatively better motor response than LD+DDCI along with longer duration of the on state by about 45 minutes and fewer dyskinesias. "
* Preparation (MP powder) *
"...we roasted MP seeds in a pan for 15 minutes; we then peeled off the teguments and ground the seeds in a small grinder; we finally passed the ground seeds through a sieve to obtain the powder, which we added to water.
* Levodopa Concentration (MP powder) *
"...we measured the content in levodopa of the Bolivian black ecotype (used in the present study) and found it to be 5.7% ..."
* Safety *
"Dyskinesias at 90 minutes were fewer with MP-Hd and LD−DDCI than with LD+DDCI. We did not find any differences among LD+DDCI, MP-Ld, and MP+DDCI.
No major Adverse events (AEs) occurred and no patients dropped out of the study protocol. When compared to LD+DDCI, the number of AEs was significantly lower with MP-Ld, and we found a trend towards reduced AEs with MP-Hd ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articl...
. AEs most commonly occurred within 30–45 minutes after treatment administration and lasted <15 minutes, except for 4 patients, who reported AEs lasting >90 minutes after LD−DDCI
* Side Effects *
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articl...
Sleepiness (somnolence) :
- 9, Levodopa
- 6, Levodopa + DDCI
- 1, MP-low dose
- 1, MP-high dose
Nausea :
- 6, Levodopa
- 2, MP-high dose
- 1, MP-low dose
Dizziness :
- 3, Levodopa
- 1, Levodopa + DDCI
Prolonged Adverse Events ( >90min) :
- 4, Levodopa
Update 2018: Similar Trial with Carbidopa (CD) instead of Benserazide reported gastrointestinal issues
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/293...
"Daily intake of MP was associated with a variable clinical response, especially in terms of tolerability. Seven patients (50%) discontinued MP prematurely due to either gastrointestinal side-effects (n = 4) or progressive worsening of motor performance (n = 3), while nobody discontinued during the LD/CD phase. In those who tolerated MP, clinical response to MP was similar to LD/CD on all efficacy outcome measures."