simonsfoundation.org/2023/0...
SNIP, with my emphasis \\
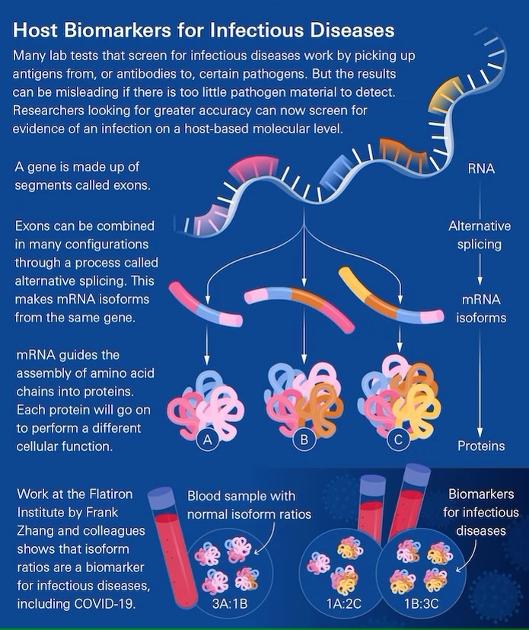
Most existing COVID-19 tests “rely on the same principle, which is that you have accumulated a detectable amount of viral material, for example, in your nose,” says study lead author Frank Zhang, who worked on the project as a Flatiron research fellow at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Biology (CCB) in New York City. “That poses a challenge when it’s early in the infection time window and you haven’t accumulated a lot of viral material, or you’re asymptomatic.”
The new technique is instead based on how our bodies mount an immune response when invaded by SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. When the assault starts, specific genes turn on. Segments of those genes produce mRNA molecules that guide the building of proteins. The particular blend of those mRNA molecules changes the types of proteins produced, including proteins involved in virus-fighting functions. The new method can confidently identify when the body is mounting an immune response to the COVID-19 virus by measuring the relative abundance of the various mRNA molecules. The new study is the first to use such an approach to diagnose an infectious disease.
\\
When put to the test using real-world blood samples, the new method yielded an impressive 98.4 percent accuracy rating. That’s especially impressive as the approach works just as well on asymptomatic patients, for whom rapid antigen tests can be less than 60 percent accurate.
\\
The new approach isn’t ready for prime time yet, Zhang says. He and his colleagues only tested blood samples rather than the nasal samples that are more common and convenient for diagnosing COVID-19. Also, they need to make sure they can distinguish between the body’s reaction to COVID-19 and its response to infections caused by other viruses, such as colds.
\\
Not ready yet, but if this approach can adapt to a more workable format i.e. nasal swabs (finger prick blood samples?) it would provide the means to detect many more potential COVID spreaders than has been possible with current testing methods. And presumably the same technique could be used in the management of viral outbreaks in the future.