This research appears to be a major breakthrough in our understanding of PCa's development and progression. It is also new evidence that further validates Dr. Abraham Morgantaler's testosterone "Saturation Model" and the underlying principles that make BAT effective. There is much in the Nature Communications paper (linked below) to digest, as it suggests a major departure from current SOC.
Maybe one day SOC advocates will wake-up to the fact that, as a long-term treatment, ADT with its uniformly debilitating QOL effects, is, as Morgantaler has long claimed, based on a flawed understanding of testosterone's effect on PCa development and progression. (BTW, our old "friends", mTOR and c-MYC are both major role-players in these new findings.)
This is a "must read" paper that all PCa patients should study and share widely.
* * *
Study Solves Testosterone’s Paradoxical Effects in Prostate Cancer, Duke Health, Published September 04, 2024 | Updated September 04, 2024
DURHAM, N.C. – A treatment paradox has recently come to light in prostate cancer: Blocking testosterone production halts tumor growth in early disease, while elevating the hormone can delay disease progression in patients whose disease has advanced.
The inability to understand how different levels of the same hormone can drive different effects in prostate tumors has been an impediment to the development of new therapeutics that exploit this biology.
Now, a Duke Cancer Institute-led study, performed in the laboratory of Donald McDonnell, Ph.D. and appearing this week in Nature Communications, provides the needed answers to this puzzle.
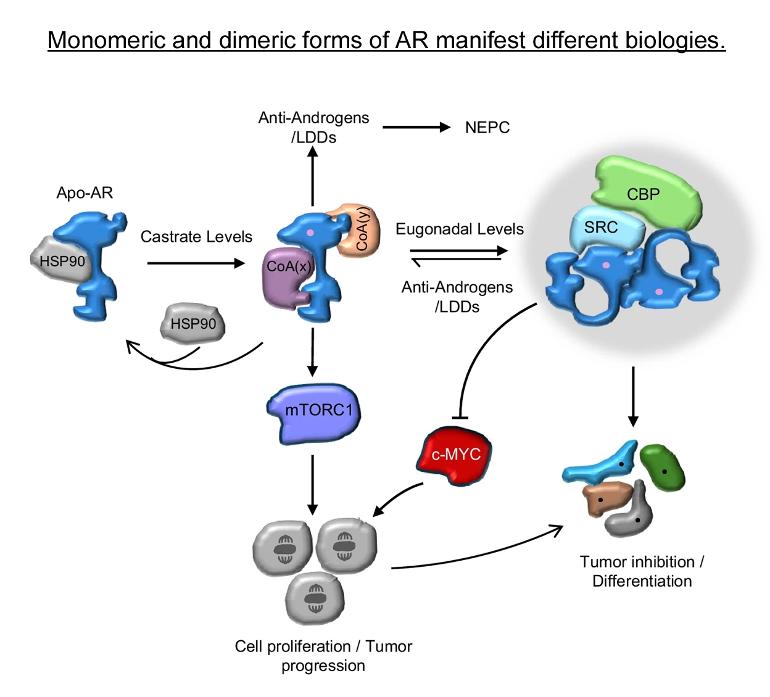
The researchers found that prostate cancer cells are hardwired with a system that allows them to proliferate when the levels of testosterone are very low. But when hormone levels are elevated to resemble those present in the normal prostate, the cancer cells differentiate.
“For decades, the goal of endocrine therapy in prostate cancer has been to achieve absolute inhibition of androgen receptor function, the protein that senses testosterone levels,” said lead investigator Rachid Safi, Ph.D., research assistant professor in the Department of Pharmacology and Cancer Biology, at Duke University School of Medicine.
“It’s been a highly effective strategy, leading to substantial improvements in overall survival,” he said. “Unfortunately, most patients with advanced, metastatic disease who are treated with drugs to inhibit androgen signaling will progress to an aggressive form of the disease for which there are limited therapeutic options.”
Using a combination of genetic, biochemical, and chemical approaches, the research team defined the mechanisms that enable prostate cancer cells to recognize and respond differently to varying levels of testosterone, the most common androgenic hormone.
It turned out to be rather simple. When androgen levels are low, the androgen receptor is encouraged to “go solo” in the cell. In doing so, it activates the pathways that cause cancer cells to grow and spread. However, as androgens rise, the androgen receptors are forced to “hang out as a couple,” creating a form of the receptor that halts tumor growth.
“Nature has designed a system where low doses of hormones stimulate cancer cell proliferation and high doses cause differentiation and suppress growth, enabling the same hormone to perform diverse functions,” McDonnell said.
In recent years, clinicians have begun treating patients with late-stage, therapy resistant prostate cancers using a monthly, high-dose injection of testosterone in a technique called bi-polar androgen therapy, or BAT. The inability to understand how this intervention works has hindered its widespread adoption as a mainstream therapeutic approach for prostate cancer patients.
“Our study describes how BAT and like approaches work and could help physicians select patients who are most likely to respond to this intervention,” McDonnell said. “We have already developed new drugs that exploit this new mechanism and are bringing these to the clinic for evaluation as prostate cancer therapeutics.”
In addition to McDonnell and Safi, study authors include Suzanne E. Wardell, Paige Watkinson, Xiaodi Qin, Marissa Lee, Sunghee Park, Taylor Krebs, Emma L. Dolan, Adam Blattler, Toshiya Tsuji, Surendra Nayak, Marwa Khater, Celia Fontanillo, Madeline A. Newlin, Megan L. Kirkland, Yingtian Xie, Henry Long, Emma Fink, Sean W. Fanning, Scott Runyon, Myles Brown, Shuichan Xu, Kouros Owzar, and John D. Norris.
The study received funding support from the National Cancer Institute (R01-CA271168, P30CA014236) and the North Carolina Biotechnology Center.
* * *
Here is the Abstract section and a link to the Duke-led study (open access) published in Nature Communications on 03 Sept 2024:
Androgen receptor monomers and dimers regulate opposing biological processes in prostate cancer cells, Nature Communications, Volume 15, Article number: 7675 (2024), Published: 03 September 2024.
Abstract
Most prostate cancers express the androgen receptor (AR), and tumor growth and progression are facilitated by exceptionally low levels of systemic or intratumorally produced androgens. Thus, absolute inhibition of the androgen signaling axis remains the goal of current therapeutic approaches to treat prostate cancer (PCa). Paradoxically, high dose androgens also exhibit considerable efficacy as a treatment modality in patients with late-stage metastatic PCa. Here we show that low levels of androgens, functioning through an AR monomer, facilitate a non-genomic activation of the mTOR signaling pathway to drive proliferation. Conversely, high dose androgens facilitate the formation of AR dimers/oligomers to suppress c-MYC expression, inhibit proliferation and drive a transcriptional program associated with a differentiated phenotype. These findings highlight the inherent liabilities in current approaches used to inhibit AR action in PCa and are instructive as to strategies that can be used to develop new therapeutics for this disease and other androgenopathies.
* * *
Androgen receptor monomers and dimers regulate opposing biological processes in prostate cancer cells, Nature Communications, Volume 15, Article number: 7675 (2024), Published: 03 September 2024.
nature.com/articles/s41467-...
* * *
And for anyone not yet familiar with the visionary work of Dr. Morgantaler, this Grand Rounds interview by GRU contributing editor Neil H. Baum, MD, and the GRU page linking his "Review Trilogy" at the 3rd Annual Meeting of the Androgen Society (from 2021) will reveal the nature of his work and how long it has taken for the value of his work to be recognized by his peers.
Testosterone Therapy in Clinical Medicine: Interview with Abraham Morgentaler, MD, FACS, Grand Rounds in Urology, Feb 24, 2023.
youtube.com/watch?v=Nemzbt6...
Androgen Society 3rd Annual Meeting Review with Abraham Morgentaler, MD, FACS, 3rd Annual Androgen Society meeting, May 2021.
grandroundsinurology.com/an...
* * *
Keep it S&W,
Ciao - cujoe