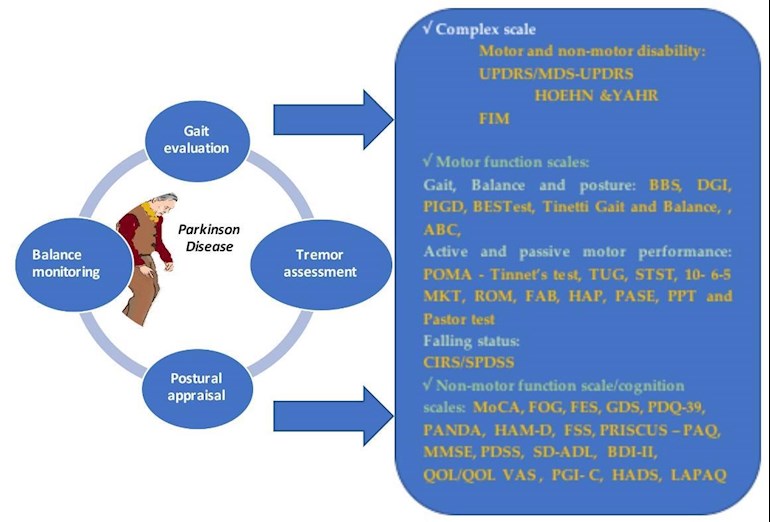
Physical therapy in all its forms has clear beneficial effects in the motor and cognition rehabilitation of Parkinson’ disease.
It is worth mentioning that the types of approached therapies led to significant improvements in gait, including improvements in speed, cadence, velocity, strength step, and turning training, balance, postural reflexes, range of motion, breathing, swallowing, mimic, writing and speech therapy, as well as a delay in freezing of gait and cognitive functions.
The continuation of the classic physical therapy is recommended, but with a decrease in the
duration and increase in the frequency of the exercises, especially ADL (Activities of Daily Living) , which allows the modulation of household activities.