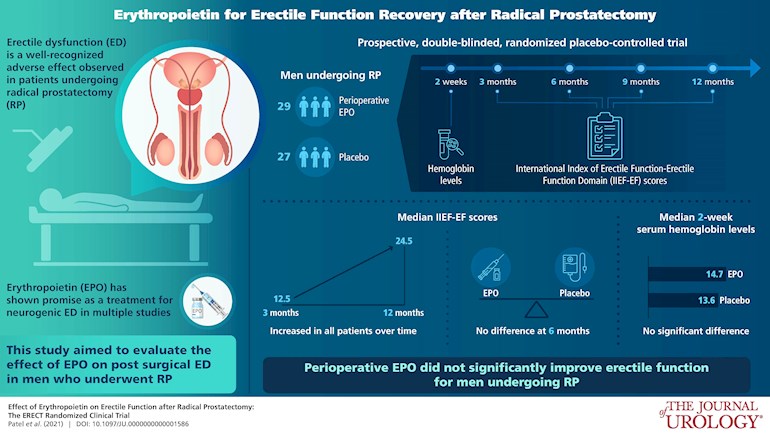
Results of a small study on the effects of the use of drug Erythropoietin prior to radical prostatectomy to improve erectile function after surgery. No positive benefit shown and the study seems to confirm that a good surgeon who can spare the nerves (that's why it's called nerve-sparing surgery) is the best route to good post-surgery erectile function.
Abstract is reproduced below:
* * *
Purpose:
Erectile dysfunction significantly impacts quality of life for men undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. Erythropoietin is a promising neurotrophic factor for neurogenic erectile dysfunction based on preclinical and retrospective data.
Materials and Methods:
ERECT (NCT00737893) is a phase 2, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (July 2017–December 2019) evaluating the impact of perioperative erythropoietin on recovery of erectile function and other patient-reported, health-related quality of life outcomes after bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy (3, 6, 9, and 12 months). Erythropoietin (20,000 units) or saline placebo was injected subcutaneously the day before, day of, and day after surgery for 3 total doses.
Results:
Of 63 patients assessed for eligibility, 56 patients were randomized. Arms (29 erythropoietin, 27 placebo) were well balanced (89.3% robotic, median age 55.5 years). International Index of Erectile Function-Erectile Function Domain (IIEF-EF) scores increased from median 12.5 at 3 months to 24.5 at 12 months. Median 2-week serum hemoglobin was higher for the erythropoietin arm compared to placebo (14.7 vs 13.6, p=0.02). There was no statistically significant difference in IIEF-EF scores at 6 months comparing erythropoietin to placebo (p=0.50) or at other time points (mixed model regression coefficient: −1.7, 95% CI −6.1–2.7, p=0.45). Excellent nerve-sparing rating (10/10) was associated with improved IIEF-EF recovery (+5.2, p=0.022). Other patient-reported, health-related quality of life domains as well as oncologic outcome and complications were similar between arms during followup.
Conclusions:
In the context of brief perioperative dosing, erythropoietin did not improve recovery of erectile function for men undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer compared to placebo. Further research to identify effective adjuncts to improve health-related quality of life for these men is needed.
* * *
Study is here:
Effect of Erythropoietin on Erectile Function after Radical Prostatectomy: The ERECT Randomized Clinical Trial
auajournals.org/doi/10.1097...
Finding an experienced surgeon with a good track record is still always the best route to a good outcome. Stay Safe & Well - K9