1. Extra-prostatic extension can be further classified as focal or extensive (also referred to as 'established' or 'nonfocal'). Focal is defined as extra-prostatic glands which occupy no more than one high power field on no more than two sections. Extensive EPE represents anything more than this.
2. Lymphovascular invasion is an independent predictor of prostate-specific antigen failure after radical prostatectomy in patients with pT3aN0 prostate cancer.
3. Percent of Gleason Pattern 4 and 5: Conclusion: The combined percentage of Gleason patterns 4 and 5 is one of the most powerful predictors of patient outcome, and appears superior to conventional Gleason score in identifying patients at increased risk of disease progression. On the basis of our results, we recommend that the combined percentage of Gleason patterns 4 and 5 be evaluated in radical prostatectomy specimens. The amount of high-grade cancer in a prostatectomy specimen should be taken into account in therapeutic decision making and assessment of patient prognosis.
a. The increased percent Gleason 4/5 was associated with older age, higher preoperative serum PSA level, higher pathologic stage, positive surgical margins, extra-prostatic tumor extension, higher Gleason score, perineural invasion, and lymph node metastasis (Table 1). The high‐grade cancer proportion (the percent Gleason pattern 4/5) demonstrated no association with prostate weight or high‐grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN).
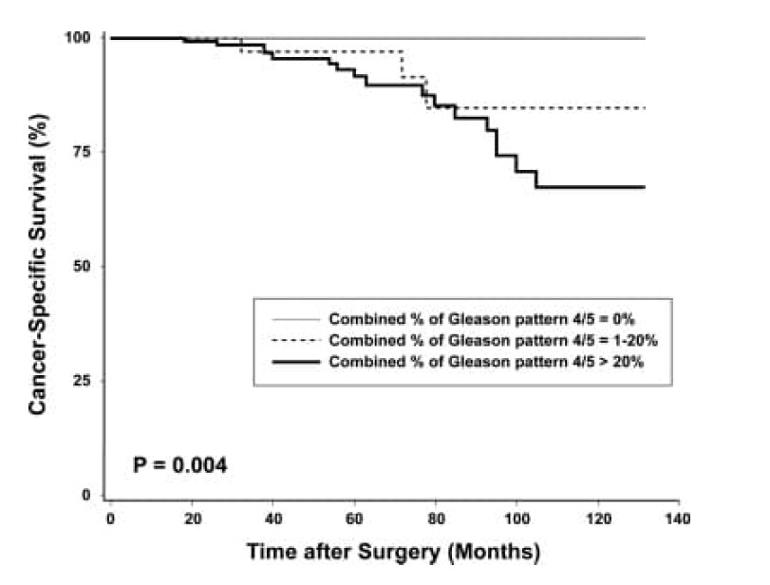
b. In a study by Cheng et al. involving 504 men who underwent radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer, the rates of 10-year cancer-specific survival were 100%, 85%, and 67% in those with 0% Gleason pattern 4/5, 1–20% Gleason pattern 4/5, and >20% Gleason pattern 4/5, respectively (17). Thus, in these 504 patients, the combined percent Gleason patterns 4 and 5 were found to be an independent predictor of cancer-specific survival.
4. In pathology, perineural invasion, abbreviated PNI, refers to the invasion of cancer to the space surrounding a nerve. It is common in head and neck cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
a. Perineural invasion (PNI) can be found in a variety of malignant tumors. It is a sign of tumor metastasis and invasion and portends the poor prognosis of patients.
b. Perineural invasion means that cancer cells were seen surrounding or tracking along a nerve fiber within the prostate. When this is found on a biopsy, it means that there is a higher chance that the cancer has spread outside the prostate.
5. Isolated high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) is detected in an average of 9% of prostate biopsies. The incidence, extent, and volume of HGPIN increase with patient age; its presence precedes the onset of prostatic carcinoma by 5 to 10 years or more.
6. Decipher testing : details on testing and meaning of results