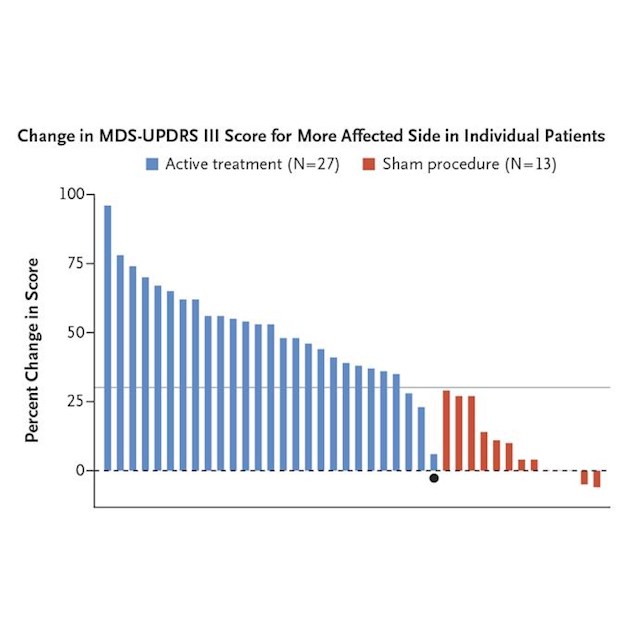
TAmong 40 enrolled patients, 27 were assigned to focused ultrasound subthalamotomy (active treatment) and 13 to the sham procedure (control). The mean MDS-UPDRS III score for the more affected side decreased from 19.9 at baseline to 9.9 at 4 months in the active-treatment group (least-squares mean difference, 9.8 points; 95% confidence interval [CI], 8.6 to 11.1) and from 18.7 to 17.1 in the control group (least-squares mean difference, 1.7 points; 95% CI, 0.0 to 3.5); the between-group difference was 8.1 points (95% CI, 6.0 to 10.3; P<0.001). Adverse events in the active-treatment group were dyskinesia in the off-medication state in 6 patients and in the on-medication state in 6, which persisted in 3 and 1, respectively, at 4 months; weakness on the treated side in 5 patients, which persisted in 2 at 4 months; speech disturbance in 15 patients, which persisted in 3 at 4 months; facial weakness in 3 patients, which persisted in 1 at 4 months; and gait disturbance in 13 patients, which persisted in 2 at 4 months. In 6 patients in the active-treatment group, some of these deficits were present at 12 months.
CONCLUSIONS
Focused ultrasound subthalamotomy in one hemisphere improved motor features of Parkinson’s disease in selected patients with asymmetric signs. Adverse events included speech and gait disturbances, weakness on the treated side, and dyskinesia. (Funded by Insightec and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number,