Hey all.
I was researching B5 metabolism genetic diseases as I think I have one, and realised the symptoms are a lot like Parkinsons. The diseases are PKAN, and coase also called NBIA- neuro degenerative associated brain iron accumulation -caused by broken enzymes converting B5 aka pantothenic acid into co-enzyme A.
Here are the symptoms-
described a kindred ascertained through a 68-year-old man who died after 13 years of progressive dementia, rigidity, bradykinesia, mild tremor, stooped posture, slow and shuffling gait, dystonia, blepharospasm, apraxia of eyelid opening, anarthria, aphonia, and incontinence.
omim.org/clinicalSynopsis/2...
NEURODEGENERATION WITH BRAIN IRON ACCUMULATION 1; NBIA1
INHERITANCE
- Autosomal recessive
HEAD & NECK
Face
- Facial grimacing
Eyes
- Pigmentary retinopathy (more common in classic disease)
- Retinal degeneration
- Optic atrophy
- Blepharospasm
- Apraxia of eyelid opening
ABDOMEN
Gastrointestinal
- Feeding difficulties
- Dysphagia
GENITOURINARY
Bladder
- Incontinence
SKELETAL
Feet
- Foot deformity
SKIN, NAILS, & HAIR
Skin
- Skin pigmentation
MUSCLE, SOFT TISSUES
- Decreased muscle mass
- Myopathic changes on pathology
NEUROLOGIC
Central Nervous System
- Psychomotor delay
- Extrapyramidal syndrome
- Involuntary movements
- Gait abnormalities
- Walking on toes
- Corticospinal signs (87% of patients in 1 report)
- Ataxia
- Choreoathetosis
- Dystonia
- Motor 'tics'
- Difficulty writing
- Rigidity
- Parkinsonism
- Orofacial dyskinesia
- Akinesia
- Spasticity
- Stiffness
- Tremor
- Dysarthria
- Speech abnormalities (palilalia)
- Cognitive decline
- Dementia, progressive
- Generalized brain atrophy
- Neuroaxonal degeneration in the brain
- Axonal swelling or thickening in the CNS
- Axonal 'spheroid' inclusions in the CNS
- Iron deposits in the globus pallidus, caudate, and substantia nigra
- MRI shows decreased signal intensity in the pallidal nuclei with central hyperintensity ('eye of the tiger' sign)
Behavioral Psychiatric Manifestations
- Psychiatric abnormalities (more common in patients with atypical disease and slow progression)
- Obsessive-compulsive trait
- Depression
- Hyperactivity
- Behavioral problems
VOICE
- Dysphonia
MISCELLANEOUS
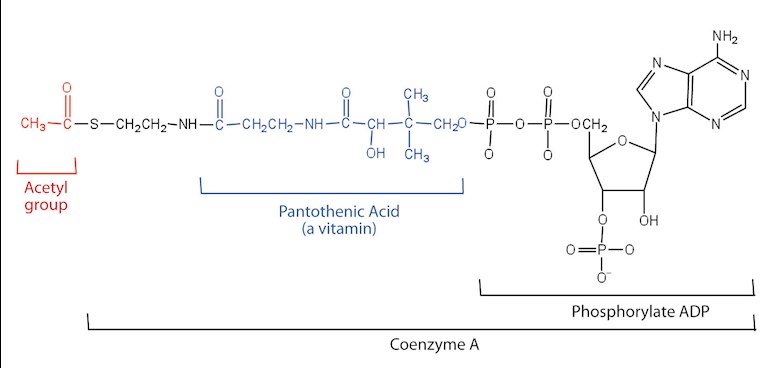
B5 aka pantothenic acid or pantothenate is needed to make COA as can be seen in the photo.
Here is a quote from a study showing just how important co enzyme a is
Coenzyme A biosynthesis: an antimicrobial drug target
A survey of the BRENDA database (
brenda-enzymes.info/) of all known enzyme activities shows
that 9% of the approximately 3500 identified activities use
CoA or a CoA thioester as a cosubstrate (E. Strauss, personal communication)
B5 is also needed to make steroid hormones in the adrenal glands, and studies increase adrenal hormone synthesis in deficient states.
It is used to treat acne, and grey hair also.
There is a few different forms of B5 supplements-
Pantothenate aka pantothenic acid. Up to 10grams a day is used in studies on acne with no side effects. Commonly sold.
Pantethine- two molecules of panteTHEINE bonded together. Breaks down into pantETHEINE in the body which feeds into B5 metabolism pathway further along than pantothenic acid. Also lowers blood cholesterol in studies (see all the positive reviews on amazon.com about people lowering their cholesterol with it). Is better than pantothenic acid in studies.
Pantethenol. Analog of of pantothenic acid. Converts to pantothenic acid in the body. Causes urinary excretion 10-50 times higher than normal values of pantothenic acid. It is sold as cosmetic product for hair, and skin. Comes as D or D, and L mixed form. The D form converts to pantothenic acid the L form does not so I assume is just peed out of the body. If only D form it can be 50:50 mixed with propylene glycol (safe) or 75:25 mixed with water or 99% pure.
Phosphopantothenic acid. Only available from chemical suppliers. This is the first thing pantothenic acid converts into in the body.
Coenzyme a- the form of B5 in food. Is 57,000 USD a kg lol or 275 USD a gram so not really viable to take as a supplement.
Here is a drop box with studies etc on B5. In he chart section is info on how b5 is converted in the body.
dropbox.com/sh/43mt92yyvshm...
High food sources are shiitake mushrooms dried, rice bran, yeast.
In conclusion B5 deficiency may be the cause, and taking B5 may be the cure of Parkinsons.
more info copy pasted from one of the PDFS in the drop box
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Cristiana Paul, M.S.
Fostering knowledge among health professionals and the public that natural therapies
exist to prevent and support a wide range of ailments while facilitating the integration
of scientifically valid research supporting these therapies in clinical practice.
®
Alcohol Detoxification
Participates in the metabolism of acetaldehyde, a by product of ethanol metabolism4, 5, 10
Anti-stress Effect
Synthesis of steroid hormones and proper functioning of the adrenal glands9
Biochemical Reactions
Coenzyme A (CoA), which is the active form of pantothenic acid, helps transfer two-carbon units (acetyl groups) in a
wide variety of biochemical reactions.12
Cholesterol and Tryglicerides lowering
Pantethine, a metabolite of pantothenic acid,18 seems to have a beneficial effect on triglyceride and lipoprotein levels by
producing cystamine. The hydrolysis product cystamine inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which in turn reduces
triglyceride synthesis. Pantethine might also reduce cholesterol synthesis by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, by
inhibiting the conversion of lanosterol to cholesterol.21, 22
Energy Metabolism
Enhances the release of energy from carbohydrates in the Krebs cycle12, 17
Fat Synthesis
Involved in synthesis of phospholipids, fats, cholesterol, and bile acids12
Fighting infections
Was shown to help the immune system fight viral hepatitis11
Neurotransmitter Synthesis
Involved in synthesis of acetylcholine12
Red Blood Cells
Involved in synthesis of porphyrin in the hemoglobin of red blood cells12
Surgery And Wound Healing
In combination, pantothenic acid and ascorbic acid significantly enhance post surgical therapy and wound healing.6, 15
Another study found that vitamin B5 accelerated the healing process of conjunctiva and the cornea after reconstructive
surgery of the epithelium.7 Pantothenic acid also appears to be essential to normal epithelial function.16
RESEARCH PROVEN BENEFITS
PDosage/Administration: ORAL
LIKELY SAFE when used orally and appropriately. Amounts up to
10 grams have been ingested without significant adverse effects.
PREGNANCY/LACTATION: LIKELY SAFE when used orally in
amounts not exceeding the recommended daily allowance (RDA).
The RDA during pregnancy/lactating is 6/7 mg. There is insufficient
reliable information about the safety of using pantothenic acid in
amounts exceeding the RDA during pregnancy/lactating; avoid
using.
Interactions with Herbs & Supplements/Drugs: None known.
Do not take pantothenic acid if you have the blood disorder called
hemophilia. It can increase the risk of bleeding.
“Study of the corticosteroid content in the adrenals and blood of rats
under pantothenate deficiency has demonstrated a decrease in
adrenocortical function. A single administration of pantothenate in a
dose of 3.3 mg/kg reduced the influence of hypovitaminosis on the
adrenals. The pantothenate derivatives (pantethine, 4'-phosphopantothenate and CoA in particular) injected to intact animals in a
single dose equimolar to 3.3 mg/kg calcium pantothenate per kg bw
had a marked steroidogenous effect.”13
“The effect of calcium D-pantothenate on the migration, proliferation and protein synthesis of human dermal fibroblasts from three
different donors was investigated. The migration of cells into a
wounded area was dose-dependently stimulated by Ca D-pantothenat.....The protein synthesis was modulated, since two unidentified
proteins were more strongly expressed in pantothenate supplemented
cultures. In conclusion, Ca D-pantothenate accelerates the wound
healing process by increasing the number of migrating cells, their
distance and hence their speed. In addition, cell division is increased
and the protein synthesis changed. These results suggest that higher
quantities of pantothenate are locally required to enhance wound
healing.”15
“The antitoxic effect of preparations of pantothenic acid is not mediated by CoA-dependent reactions of detoxication, but most probably
is due to intensification of ET (ethanol) oxidation and perhaps to its
elimination from the organism.”10
“Increased cytoplasmic synthesis of CoA by addition of 5 mM
pantothenate (vitamin B5) increased the thermogenic response to
glucose more in mdx than in control muscles. We conclude that the
low energy turnover in mdx-mouse muscle fibres is not due to a
decrease of intracellular glucose availability, but rather to a decreased
oxidative utilization of glucose and free fatty acids. We suggest that
some enzyme complex of the tricarboxylic acid cycle or inefficiency
of CoA transport in the mitochondria could be involved.”17
“27 diabetics (15 NIDDM and 12 IDDM) with dyslipidemia (14
type IV, 8 type IIa and 5 type IIb) were divided in 3 groups and
treated with 3 different hypolipemic drugs (Group A: pantethine 600
mg/day…. Pantethine and acipimox were more effective on triglycerides (-37.7% and -23.3% respectively).”18
TO CONTACT DESIGNS FOR HEALTH, PLEASE CALL US AT
(800) 847-8302, OR VISIT US ON THE WEB AT
WWW.DESIGNSFORHEALTH.COM.
References
1. Bertolini S, et al. Lipoprotein Changes Induced by Pantethine in Hyperlipoproteinemic
Patients: Adults and Children. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. Nov1986;24(11):630-37.
2. Donati C, et al. Pantethine, Diabetes Mellitus and Atherosclerosis. Clinical Study of 1045
Patients. Clin Ter. Mar1989;128(6):411-22.
3. Coronel F, et al. Treatment of hyperlipemia in diabetic patients on dialysis with a
physiological substance. Am J Nephrol. 1991;11(1):32-6.
4. Moiseenok AG, et al. The Protective Effect of Pantothenic Acid Derivatives and Changes in
the System of Acetyl CoA Metabolism in Acute Ethanol Poisoning. Farmakol Toksikol.
Oct1988;51(5):82-86.
5. Chernikevich IP, et al. Possible ways of regulating detoxifying processes in the alcohol
dehydrogenase reaction with pantothenic acid derivatives. Vopr Med Khim. Mar1993;39(2):
38-40.
6. Lacroix B, et al. Role of Pantothenic and Ascorbic Acid in Wound Healing Processes: In
Vitro Study on Fibroblasts. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1988;58(4):407-13.
7. Raczynska K, Iwaszkiewicz-Bilikiewicz B, Stozkowska W, Sadlak-Nowicka J. Clinical
evaluation of provitamin B5 drops and gel for postoperative treatment of corneal and
conjuctival injuries. Klin Oczna. 2003;105(3-4):175-8.
8. Calcium pantothenate in arthritic condtions. A report from the General Practitioner
Research Group. Practitioner. 1980;224:208-211.
9. Fidanza A. Therapeutic action of pantothenic acid. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 1983;suppl 24:53-
67 [review].
10. Moiseenok AG, Dorofeev BF . The protective effect of pantothenic acid derivatives and
changes in the system of acetyl CoA metabolism in acute ethanol poisoning. Farmakol
Toksikol. 1988 Sep-Oct;51(5):82-6.
11. Komar VI.The use of pantothenic acid preparations in treating patients with viral hepatitis
A. Ter Arkh. 1991;63(11):58-60
12. Murray R.K, , Granner D. K., Harper's Biochemistry, 23-rd edition
13. Tarasov IuA, Sheibak VM Adrenal cortex functional activity in pantothenate deficiency and
the administration of the vitamin or its derivatives. Vopr Pitan. 1985 Jul-Aug;(4):51-4.
14. Schwabedal PE, Pietrzik K . Pantothenic acid deficiency as a factor contributing to the
development of hypertension. Cardiology. 1985;72 Suppl 1:187-9.
15. Weimann BI, Hermann D.Studies on wound healing: effects of calcium D-pantothenate on
the migration, proliferation and protein synthesis of human dermal fibroblasts in culture. Int
J Vitam Nutr Res. 1999 Mar;69(2):113-9.
16. McKevoy GK, ed. AHFS Drug Information. Bethesda, MD: American Society of HealthSystem Pharmacists, 1998.
17. Even PC, Decrouy A Defective regulation of energy metabolism in mdx-mouse skeletal
muscles. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304 ( Pt 2):649-54.
18. Tonutti L, Taboga C . Comparison of the efficacy of pantethine, acipimox, and bezafibrate
on plasma lipids and index of cardiovascular risk in diabetics with dyslipidemia. Minerva
Med. 1991 Oct;82(10):657-63
19. Gaddi A, Descovich GC Controlled evaluation of pantethine, a natural hypolipidemic
compound, in patients with different forms of hyperlipoproteinemia. Atherosclerosis. 1984
Jan;50(1):73-83.
20. Arsenio L, Bodria P .Effectiveness of long-term treatment with pantethine in patients with
dyslipidemia. Clin Ther. 1986;8(5):537-45.
21. Cighetti G, Del Puppo M .Modulation of HMG-CoA reductase activity by
pantetheine/pantethine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 25;963(2):389-93.
22. Wittwer CT, Graves CP .Pantethine lipomodulation: evidence for cysteamine mediation in
vitro and in vivo. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Nov;68(1-2):41-9.
“A one-year clinical trial with pantethine (a metabolite of Pantothenic
acid) was conducted in 24 patients with established dyslipidemia….
Blood lipid assays repeated after 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months of treatment revealed consistent and statistically significant reductions of all
atherogenic lipid fractions (total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B) with parallel increases of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein A. The results were
equally good in patients with uncomplicated dyslipidemia and in
those with associated diabetes mellitus. The authors conclude that
pantethine (a drug entity related to the natural compound, pantetheine) represents a valid therapeutic support for patients with dyslipidemia not amenable to satisfactory correction of blood lipids by diet
alone.”20
“Pantethine (P), (a metabolite of Pantothenic acid) and major
component and precursor of coenzyme A, was evaluated within a
double-blind protocol (8 weeks for P or for a corresponding placebo)
in 29 patients, 11 with type IIB hyperlipoproteinemia, 15 with type
IV, and 3 with an isolated reduction of high density lipoprotein
cholesterol (HDL-C) levels……..P (300 mg t.i.d.) determined a
highly significant lowering of plasma total and low density lipoprotein (LDL) associated cholesterol (-13.5% for both parameters)….. In
the same patients, HDL-C levels increased about 10% at the end of
treatment. …..plasma triglyceride levels were reduced around
30%....This study provides evidence for a significant hypocholesterolemic effect of P, a natural compound free of overt side effects. It
also indicates that P may raise HDL-C levels in type IIB patients,
while moderately reducing triglyceridemia.”19