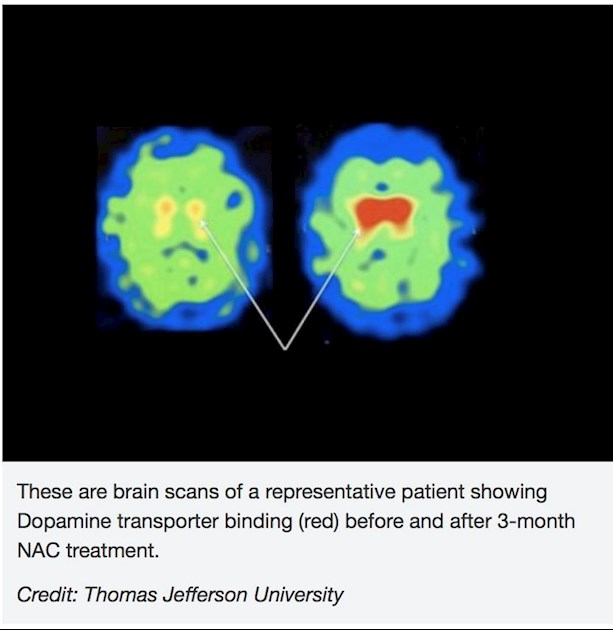
The results of this small, preliminary study demonstrate for the first time a potential direct effect of NAC, N-Acetyl Cysteine, on the dopamine system in PD patients, and this observation may be associated with positive clinical effects (about 12%). Here are a few details published from this earlier, small NAC trial:
The overarching goal of this pilot study (which was small but included humans) was to generate additional data about potentially protective properties of NAC in PD, using an in vitro and in vivo approach. The results of this small study of PD patients suggest that NAC might be useful in increasing brain glutathione levels and thereby impact oxidative processes in the brain. Glutathione itself inefficiently crosses the blood-brain barrier [11], the results of this small study of PD patients suggest that NAC might be useful in increasing brain glutathione levels and thereby impact oxidative processes in the brain.
NAC is available over-the-counter as an oral supplement and also is available as an injectable pharmaceutical that is primarily used to protect the liver in acetaminophen overdose. PD patients were evaluated before and after 3 months of receiving the NAC with DaTscan to measure dopamine transporter (DAT) binding and the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) to measure clinical symptoms. Details include:
"We used the combination of oral and IV forms because oral absorption is relatively low (6–10%) and variable [8,9]. Furthermore, an MRS study of 3 patients with PD showed that blood glutathione increased after the start of an NAC infusion and reached a maximum at approximately 60 to 75 minutes [10]. Brain glutathione also increased with maximal values observed at approximately 90 to 110 minutes. Subjects who had the greatest percent change in blood glutathione after NAC infusion also had the greatest percent change in brain glutathione. Interestingly, none of the subjects returned to their baseline brain glutathione levels even at 120 minutes after NAC infusion.
Glutathione, an important reducing agent in the neurons, has been found to be depleted in the brain of PD patients [28]. The brain has difficulty withstanding substantial amounts of oxidative stress because of the presence of high amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids, low levels of antioxidants such as glutathione, and increased iron content in specific areas such as the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra (SN) [7]. Since glutathione itself inefficiently crosses the blood-brain barrier [11], the results of this small study of PD patients suggest that NAC might be useful in increasing brain glutathione levels and thereby impact oxidative processes in the brain.
An additional component to the relationship between oxidative stress and PD is related to alpha-synuclein, a prominent component of Lewy body aggregates [31] which are a pathological hallmark of PD. Previous studies have implicated the role of oxidative stress in the formation of synuclein aggregates [32,33]. In addition, several studies have suggested that iron-related oxidative stress can promote α-synuclein aggregation [34,35]. Furthermore, soluble nitrated α-synuclein, which results from interactions with oxidated nitrogen species, appears to activate microglia to produce substantial amounts of ROS through modulation of specific ion channels [36].
Thus, there appears to be growing evidence that oxidative stress likely plays a prominent role in the pathophysiology of PD. When enough oxidative stress occurs, the cell can no longer protect itself resulting in dysfunction and ultimately cell death. The question is whether interventions designed to restore the redox potential will be effective in attenuating the disease process.
The clinical component of the current study supports other preliminary work. For example, the effect of glutathione in PD was tested in a previous randomized double blind placebo controlled study of 21 PD patients that were not adequately controlled on medication showing a modest effect in symptoms that trended towards significance [53]. We theorized based on the above literature and our own studies that NAC might be more efficient. In addition, an important additional step in the current study was to go beyond a clinical measure such as the UPDRS, and evaluate DAT binding as a physiological marker. Overall, it was highly encouraging to observe substantial changes over such a short period of time, suggesting additional timelines for future studies.
It should also be noted that the current study provided the NAC as both an IV and oral supplement. It is known that the IV administration of NAC results in substantially higher concentrations of NAC in the plasma. However, it is not known whether these higher concentrations are required for any clinical or physiological effect in PD. Future studies might provide some patients with more IV doses of NAC versus only the oral NAC to determine which route and dose of administration might provide an optimal effect.
Read the full study:
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articl...
See also larger study underway: clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show...